The Evolution of Graphene Batteries in Smartphones

Picture this: You’re halfway through your day, relying on your smartphone to keep you connected, entertained, and organized. Suddenly, you’re hit with the dreaded low-battery warning — your digital lifeline precariously hanging by a thread. Sound familiar? No matter how advanced our phones have become, many still can’t last a full day without scrambling for a charger.
For years, lithium-ion batteries have been the heart powering our devices, but they come with compromises. They can be slow to charge, quick to drain, and they age faster than an avocado goes from ripe to rotten. It’s a pain point for users, and the demand for longer battery life is louder than ever. That’s where graphene batteries swagger onto the scene.
Graphene is the new kid on the block, promising to kick battery woes to the curb. Thinner than a sheet of paper yet mighty enough to supercharge battery life, graphene batteries are like the superhero version of our current power sources. They’re not just about keeping your phone alive for those extra hours; they’re about unlocking in a new era of mobile tech where ‘battery anxiety’ becomes a thing of the past. In this article, we’ll unpack why graphene is more than just buzz and how it might just be the future of smartphone batteries. Strap in — we’re about to explore how this revolutionary tech could keep our devices powered up longer and better.
What the heck is Graphene Batteries?
Graphene is pretty much the Superman of materials. It’s a single layer of carbon atoms, tightly bound in a hexagonal honeycomb lattice that’s only one atom thick. To get a picture in your head, imagine a nano-scale chicken wire made entirely of carbon atoms. This stuff is seriously strong — about 200 times stronger than steel — and it packs a punch in flexibility and conductivity. It’s also incredibly lightweight; a sheet of graphene as big as a football field would weigh less than a gram.
But what’s really got tech heads excited is its electrical superpowers. Graphene’s electrons can move about 100 times faster than they can in silicon, which is the current widely used material in electronics. This means devices will not only charge faster but could also perform a whole lot better. Plus, graphene is see-through and bends like nobody’s business, opening doors to flexible screens and other future-tech applications.
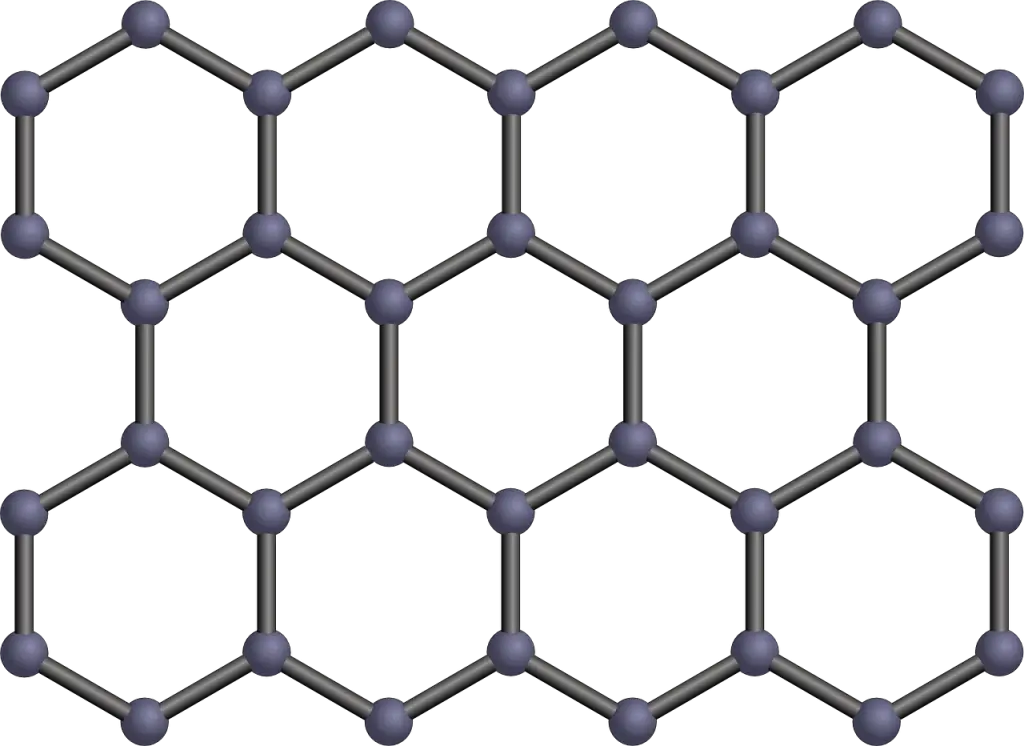
From Graphite to Graphene – The Science of Thinner and Stronger
You’ve probably got a bit of graphite hanging around in your pencil case. Well, scientists found a pretty neat party trick — they could take that same stuff and turn it into graphene. The transformation from graphite, a stack of many layers of carbon, to super-thin graphene isn’t just a magic act. It involves methods like exfoliation (basically using sticky tape to peel off layers of graphene), or chemical vapor deposition, where gasses react on a surface to leave a graphene film.
Scientists have been refining these methods to get high-quality graphene. They’re after sheets that are not only super thin but also free of any defects that could mess with performance. It’s a bit like making the world’s thinnest, strongest pancake: you’ve got to get it just right (2).
Graphene vs. Lithium-Ion
Now let’s pit graphene against the reigning champ, lithium-ion batteries. Here’s the lowdown: lithium-ion batteries are like that dependable friend who always shows up. They’ve been around since the ’90s, powering everything from your phone to electric cars. But they’ve got a few chinks in their armor. They take ages to charge, they don’t hold as much juice as we’d like, and after a while, they start losing their spark.
Enter graphene batteries. With graphene, you’re looking at batteries that can potentially charge up to five times faster than lithium-ion ones. We’re talking zero to full in the time it takes to down a coffee. Plus, they could last way longer, not just throughout the day, but over the years, too, without losing their charging mojo. And because graphene can conduct heat better, there’s less chance your phone will turn into a pocket-sized heater. The best part? These batteries could be slimmer, giving phone designers more room to play or even slimming down our devices (3).

Let’s get to the good stuff: why graphene is a game-changer for phone batteries. We’re talking about its electrical conductivity, which is just a fancy way of saying that it lets electrons zip through it with ease. This means your phone charges at breakneck speeds — you’re getting a lot more power in a lot less time. But it’s not just about speed; it’s also about efficiency. With graphene, you can say goodbye to the power drain that has you chained to the nearest outlet. Batteries with graphene are more like a marathon runner — they go the distance, holding on to power longer, and making sure your phone has the juice when you need it most.
Longevity and Durability
Durability is where graphene batteries flex their muscles. Traditional lithium-ion batteries have a kryptonite — they wear out. Each time you charge your phone, you chip away at your battery’s life. But graphene’s sturdy structure gives it a leg up. We’re looking at batteries that could last years longer than the ones we’re used to. They stand up to the wear and tear of constant charging cycles like champs, meaning your phone’s battery could stay strong from the first unboxing video to the last selfie.
Safety and Stability
No one wants their pocket to turn into a mini barbecue. Lithium-ion batteries have a rep for overheating, and in some rare cases, catching fire. Graphene, on the other hand, plays it cool — literally. It’s like the fire extinguisher of materials, spreading out the heat instead of letting it build up. This means a much lower risk of overheating, and a big nope to explosions. So, you can keep on streaming, gaming, or scrolling without that hot pocket worry. With graphene, batteries are stable, less volatile, and have your back on the safety front.

As we speak, graphene batteries aren’t just some sci-fi fantasy — they’re starting to creep into the market. While the full transition from lab to the consumer’s hand is still on the horizon, certain manufacturers are flirting with models that boast of the graphene advantage. For instance, Samsung has been toying with the idea, exploring patents that outline graphene ball materials capable of boosting battery capacity and speeding up charging times (1). Then there’s Huawei, which dipped its toes in the graphene pool by incorporating a graphene-assisted battery in the Mate 20 X, aiming to keep its cool under heavy use
But these are just baby steps. The real leap will come when a phone powered purely by a graphene battery hits our shelves — that’s when we’ll see the true mettle of this tech. And while the pickings are slim right now, the tech community is buzzing with anticipation, eager to see how these advanced power cells will revolutionize our mobile experience.
User Experiences and Performance Feedback
The proof, as they say, is in the pudding. Early adopters and tech aficionados who’ve had a taste of graphene in their gadgets are sharing promising tales. Reports suggest improved battery life and notably less anxiety about making it through the day on a single charge.
However, these are just the initial whispers from the front lines, and broader consumer feedback is needed to paint a complete picture. As more devices with graphene-based technology land in consumers’ hands, the tech community will be keeping an eagle eye on user forums, product reviews, and tech blogs for the lowdown on whether graphene lives up to its hype in daily use.
World First Mobile Phone Powered by Graphene
Xiaomi made headlines with the introduction of the Mi 10 Ultra, a device that has come closest to harnessing the full potential of graphene battery technology. Launched to commemorate the company’s 10th anniversary, the Mi 10 Ultra features a cutting-edge graphene-based lithium-ion battery, setting a new benchmark in charging speeds and efficiency. With the ability to charge at an astonishing 120W, this phone can reach 41% in just 5 minutes and a full charge in an eye-popping 23 minutes (1). This unprecedented leap forward is a glimpse into a future where waiting hours for your phone to charge could become a quaint memory. The Mi 10 Ultra isn’t just a phone; it’s a testament to the strides being made in battery technology, offering a tantalizing preview of what graphene batteries might hold for the smartphone industry as a whole.

Challenges and Limitations: Production Scalability
Scaling up production to meet global demand poses one of the most significant challenges for graphene batteries. Graphene’s extraordinary qualities stem from its ultra-thin, one-atom-thick lattice, but manufacturing it on a commercial scale is not straightforward. The transition from laboratory to factory floor involves maintaining high-quality, defect-free graphene production, which currently requires precise conditions that are difficult and expensive to replicate on a mass scale. Manufacturers are racing to refine production methods that can support the volume needed for the smartphone industry without compromising the integrity of the graphene.
Cost Implications
The financial aspect of graphene battery technology cannot be overlooked. While the cost of producing graphene has been dropping, it remains a significant barrier to replacing the current industry-standard lithium-ion cells. The synthesis of high-purity graphene is resource-intensive, and the specialized equipment and energy required for production add to the cost. These expenses will inevitably be passed on to consumers unless a cost-effective method of production is developed. As such, while the benefits of graphene batteries are numerous, the impact on the final price tag of smartphones is a critical consideration for manufacturers and consumers alike.
Technological and Commercial Hurdles
Technological and commercial barriers also stand in the way of graphene batteries becoming mainstream. Compatibility with existing smartphone designs, safety regulations, and battery life cycle management are technological challenges that need addressing. On the commercial side, the smartphone market is exceptionally competitive, and companies may be reluctant to adopt a new, unproven technology at a large scale until it has been thoroughly tested in the market. Furthermore, patenting issues and intellectual property rights can stifle innovation, as companies working on similar technologies vie for dominance. The path to widespread adoption of graphene batteries is, therefore, as much about navigating these commercial realities as it is about overcoming the technical challenges (3).
The take
The entry of graphene batteries into the smartphone realm is more than just a trivial step forward; it represents a potential revolution in how we interact with our mobile devices. The promise of faster charging times, extended battery life, and enhanced safety speaks to the core desires of smartphone users globally. Graphene’s superior conductivity and thermal management offer a tantalizing vision of a future where ‘battery anxiety’ is a thing of the past, and the need for midday charging becomes obsolete.
Yet, for all their potential, graphene batteries are not without their challenges. Mass production, cost factors, and technological integration pose significant hurdles that the industry must clear. However, the pace of innovation and the high stakes of staying competitive in the smartphone market provide strong motivation to overcome these obstacles.
As we look to the horizon, the question isn’t if graphene batteries will become the standard in mobile technology, but when. With each passing day, the technology matures, production methods improve, and the costs inch downward. As these trends continue, the likelihood increases that we will soon be powering our phones with this remarkable material.
In sum, graphene batteries stand at the precipice of changing the mobile landscape. They hold the keys to unlocking a new era of smartphone utility—one where the devices we rely on so heavily will finally be able to keep up with the demands we place on them. Looking forward, we can expect to see our relationship with mobile technology evolve in exciting ways as graphene batteries make their mark



